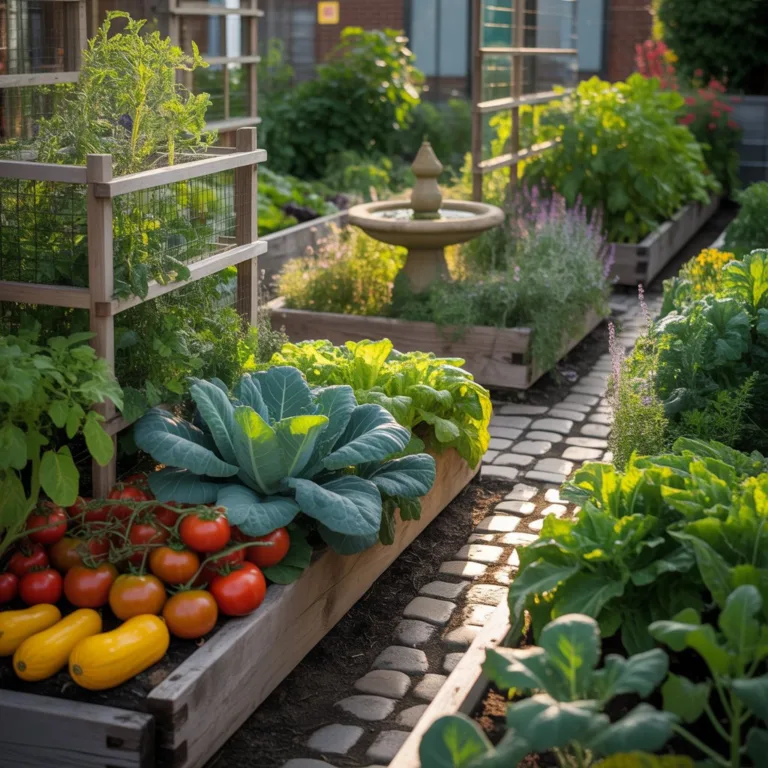
In today’s world, reducing our carbon footprint has become more important than ever. One of the most effective and enjoyable ways to achieve this is through gardening. By carefully planning our gardens and adopting eco-friendly practices, we not only create beautiful spaces but also actively contribute to environmental sustainability. How to Reduce Carbon Footprint Through Gardening involves strategic actions, from choosing the right plants to managing waste intelligently. In this article, we will explore practical tips, detailed strategies, and proven techniques to help you make your gardening practices environmentally responsible.

Understanding Carbon Footprint in Gardening
Before diving into practical steps, it’s essential to understand what a carbon footprint in gardening entails. Every activity, from buying fertilizers to watering plants, emits carbon dioxide (CO2) or other greenhouse gases. Transporting soil, purchasing pots, or using synthetic pesticides all contribute to your garden’s total emissions. By adopting sustainable methods, such as Compostagem Doméstica and horta inteligente caseira, you can significantly reduce these emissions. According to studies by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), home gardening can cut household carbon emissions by up to 20% when sustainable practices are applied effectively.
Choosing Sustainable Plants and Trees
The first step in reducing your garden’s carbon footprint is selecting the right flora. Native plants, drought-resistant varieties, and perennial species require less water, fewer fertilizers, and minimal maintenance. This approach not only saves resources but also supports local biodiversity. Experts recommend using a mix of trees and shrubs that can sequester carbon efficiently. For instance, fruit-bearing trees not only capture CO2 but also provide fresh produce, reducing your reliance on carbon-intensive grocery items. Additionally, companion planting can naturally deter pests, minimizing chemical usage and supporting a zero-waste approach in gardening.
Practical Tips for Plant Selection
- Opt for native species adapted to your climate to reduce water and fertilizer needs.
- Include nitrogen-fixing plants like legumes to naturally enrich the soil.
- Choose plants with long lifespans to minimize replacement and resource use.
- Incorporate fruit and vegetable varieties to support a home-based, low-carbon diet.
Soil Management and Composting Techniques
Healthy soil is the foundation of a low-carbon garden. Traditional gardening often relies heavily on chemical fertilizers, which contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. By practicing Compostagem Doméstica and creating nutrient-rich compost from kitchen scraps and garden waste, you can enrich your soil naturally. Composting reduces methane emissions from organic waste in landfills and enhances soil carbon storage. Another sustainable technique involves mulching, which preserves soil moisture, prevents erosion, and reduces the need for frequent watering.
Step-by-Step Guide to Home Composting
- Collect kitchen scraps, leaves, and small branches in a compost bin.
- Layer green (nitrogen-rich) and brown (carbon-rich) materials for balanced decomposition.
- Turn the compost every few weeks to aerate and speed up the process.
- Apply finished compost to your garden beds to improve fertility and soil structure.
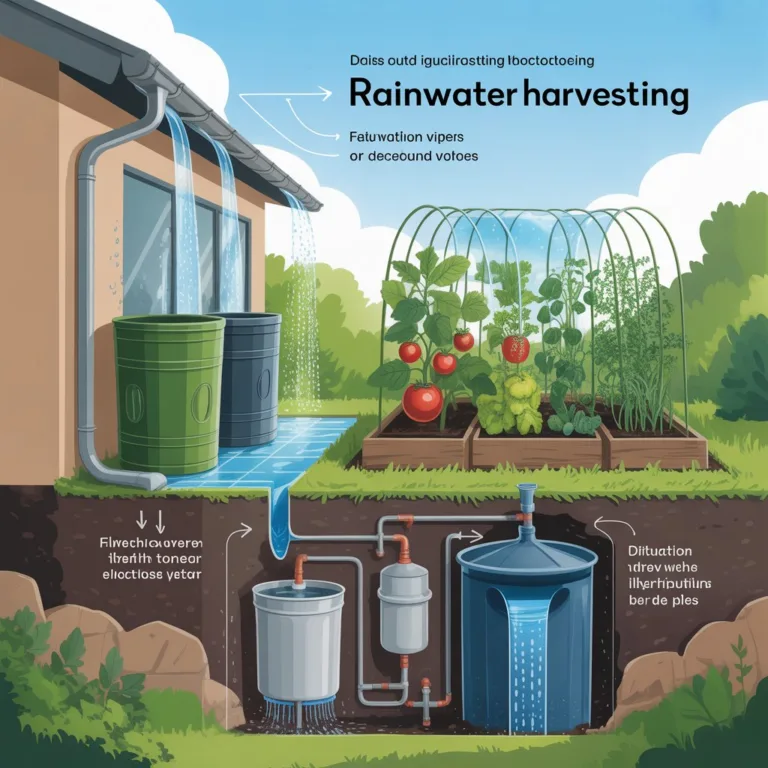
Water Conservation Strategies
Watering practices significantly impact a garden’s carbon footprint. Using conventional irrigation systems consumes energy and can contribute indirectly to CO2 emissions. Implementing water-efficient techniques such as drip irrigation, rainwater harvesting, and mulching reduces water use and energy consumption. Additionally, grouping plants according to water needs—an approach called hydrozoning—ensures optimal watering without wastage. Experts in sustainable gardening emphasize that even small changes in watering habits can reduce the overall carbon footprint while promoting healthier plant growth.
Eco-Friendly Watering Practices
- Install rain barrels to capture and reuse rainfall.
- Use drip or soaker hoses instead of sprinklers for targeted irrigation.
- Water plants early in the morning or late in the evening to reduce evaporation.
- Apply mulch around plants to retain soil moisture naturally.
Reducing Waste Through Reuse and Recycling
Reducing, reusing, and recycling materials in your garden contributes significantly to a smaller carbon footprint. Creative use of materials like pneu reutilizado for planters, madeira reutilizada for raised beds, and leftover pots and trays prevents these items from entering landfills. Additionally, practicing desperdício zero by repurposing garden waste into mulch or compost creates a circular system of resource use. This approach aligns with sustainable living principles and demonstrates conscientious consumption, which is crucial for environmental education and long-term ecological benefits.
Examples of Upcycled Garden Materials
- Old tires as self-watering planters.
- Wooden pallets turned into vertical garden structures.
- Glass jars and bottles used as seedling starters.
- Cardboard boxes layered as weed-suppressing mulch.
Energy-Efficient Gardening Practices
Gardening can also indirectly affect energy consumption and emissions. For instance, using electric or manual tools instead of gas-powered equipment reduces CO2 output. Solar-powered garden lights, rainwater pumps, and energy-efficient greenhouses are excellent alternatives that align with a low-carbon lifestyle. Planning your garden layout efficiently reduces unnecessary trips for maintenance, optimizing energy use. Experts advise integrating smart technologies where possible, combining automation with sustainable practices to minimize the overall environmental impact of gardening activities.
Energy-Saving Tips for Gardeners
- Switch to manual or electric tools to reduce fossil fuel use.
- Install solar panels for outdoor lighting and water pumps.
- Group plants logically to minimize maintenance travel and energy use.
- Use reflective mulch to optimize sunlight and reduce greenhouse heating needs.
Community Gardening and Carbon Footprint Awareness
Individual efforts are important, but community gardening initiatives amplify the impact of sustainable practices. Shared gardens encourage educação and conscientização about low-carbon living, resource efficiency, and healthy eating. Community composting programs, seed exchanges, and collaborative planting events promote a sense of collective responsibility. Studies have shown that participants in community gardens often adopt other sustainable practices in their homes, further contributing to carbon reduction. By participating in or establishing local gardening networks, you enhance both social and environmental well-being.
Benefits of Community Gardening
- Improves local air quality and reduces neighborhood carbon footprint.
- Provides access to fresh, low-carbon produce for participants.
- Encourages sustainable practices through shared knowledge and workshops.
- Fosters environmental stewardship among children and adults.
Seasonal Gardening and Carbon Reduction
Planting according to seasons can significantly reduce your garden’s carbon footprint. Seasonal gardening ensures that plants are grown under optimal natural conditions, minimizing the need for artificial heating, cooling, or lighting. For example, winter crops like kale and spinach thrive without additional energy inputs, while summer crops benefit from abundant sunlight and rainfall. Incorporating crop rotation and polyculture techniques improves soil fertility naturally and prevents pest outbreaks, further reducing reliance on chemical inputs and energy-intensive interventions.
Practical Examples of Low-Carbon Gardens
Several practical examples illustrate how How to Reduce Carbon Footprint Through Gardening can be implemented effectively:
- A backyard horta inteligente caseira using native herbs, rainwater collection, and composted soil.
- A rooftop garden with solar lighting, container recycling, and seasonal vegetables.
- Community garden with shared compost bins, fruit trees, and educational signage about low-carbon practices.
- Vertical gardens using reclaimed wood and old bottles, reducing land use and material waste.
Conclusion: Taking Action for a Sustainable Future
Reducing your carbon footprint through gardening is not only feasible but also rewarding. By adopting sustainable plant choices, soil management, water conservation, energy-efficient practices, and creative reuse of materials, you actively contribute to environmental preservation. Community initiatives amplify your efforts, creating a ripple effect of ecological consciousness. Remember, every small action counts. Start today by assessing your garden, implementing one or two low-carbon strategies, and gradually expanding your sustainable practices. Together, these steps build a greener, healthier planet for future generations.
Questions for You, the Reader
Which low-carbon gardening techniques have you tried in your home? How do you manage garden waste to minimize environmental impact? Are there local community gardens you could join to expand your sustainable practices?
FAQ
1. What is the best way to reduce water usage in gardening?
Implement drip irrigation, collect rainwater, and apply mulch to retain soil moisture. Group plants by water needs (hydrozoning) to optimize watering efficiency.
2. Can composting really reduce greenhouse gas emissions?
Yes. Composting organic waste prevents methane emissions from landfills and improves soil carbon storage, contributing to a lower carbon footprint.
3. How do native plants help in reducing carbon emissions?
Native plants require less water, fertilizers, and pesticides, reducing resource use and energy-intensive maintenance. They also support local biodiversity and carbon sequestration.
4. Is community gardening effective in carbon footprint reduction?
Absolutely. Shared gardens promote sustainable practices, composting, and local food production, collectively lowering environmental impact.
5. How can I reuse materials in my garden?
Upcycle tires, wooden pallets, glass jars, and cardboard boxes to create planters, vertical gardens, and mulch, reducing waste and emissions.
External Resources

Sofia Greenfield is a sustainable gardening expert and environmental educator who inspires families and urban gardeners to cultivate green spaces responsibly. She shares practical tips on growing vegetables, herbs, and flowers using eco-friendly and recycled materials, emphasizing the joy of gardening while protecting the planet.