Water is one of the most precious resources we have, and using it wisely in the garden is crucial for sustainability, cost savings, and healthy plants. With climate change and increasing droughts in many regions, gardeners are looking for ways to reduce water waste while maintaining lush, thriving gardens. By implementing practical techniques and smart strategies, it’s possible to conserve water without compromising plant health.

Understanding Water Waste in Gardening
Water waste often occurs in subtle ways that many gardeners don’t immediately notice. Overwatering, poor soil structure, inefficient irrigation methods, and plant choices can all contribute to unnecessary water consumption. Identifying the sources of waste is the first step in creating a more sustainable garden.
Soil plays a key role in water retention. Sandy soils drain quickly and require more frequent watering, while clay soils hold water longer but can become compacted, limiting root access. Mulching, proper plant selection, and effective irrigation systems help optimize water usage.
Choosing Water-Efficient Plants
Selecting plants that are naturally drought-tolerant or well-suited to your climate is one of the most effective ways to reduce water use. Native plants are adapted to local conditions, requiring less supplemental irrigation once established.
Tips for selecting plants:
- Drought-tolerant perennials: Lavender, sedum, and yarrow thrive with minimal water.
- Edible plants with low water needs: Certain herbs, tomatoes, and peppers can be grown with reduced irrigation.
- Groundcovers and grasses: Instead of lawns, consider groundcovers like creeping thyme or ornamental grasses that require less water.
Grouping plants with similar water needs together in zones can also prevent overwatering certain species while under-watering others. This method, known as hydrozoning, allows for more efficient irrigation management.
Soil Preparation and Improvement
Healthy soil retains moisture better, reducing the need for frequent watering. Compost and organic matter improve soil structure, enhancing its ability to hold water. Mulching with organic materials like straw, wood chips, or leaves further prevents moisture evaporation and keeps the soil temperature consistent.
Techniques for soil improvement:
- Mix compost into garden beds to enhance water retention.
- Avoid compacting soil by minimizing foot traffic in planting areas.
- Use raised beds with well-draining soil for better water control.
By focusing on soil health, gardeners can achieve better water efficiency and healthier plants, as strong roots absorb nutrients and water more effectively.
Efficient Irrigation Methods
Watering methods have a significant impact on how much water is used and lost in a garden. Drip irrigation, soaker hoses, and targeted watering techniques deliver water directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff.
Recommended practices:
- Drip irrigation: Provides a slow, steady supply of water directly to the root zone.
- Soaker hoses: Flexible hoses with tiny holes that allow water to seep into the soil evenly.
- Watering in the early morning or evening: Reduces evaporation during the hottest part of the day.
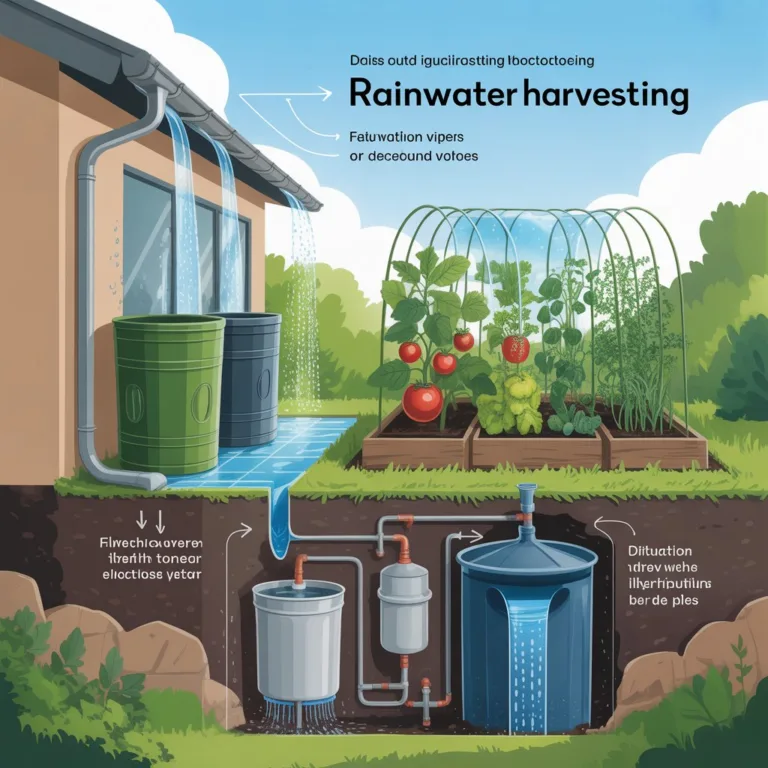
- Rainwater collection: Use barrels to capture rainwater for irrigation, reducing dependency on municipal water.
Automated irrigation timers can further ensure that plants are watered only when necessary, preventing both overwatering and under-watering.
Mulching for Moisture Retention
Mulching is an essential strategy for conserving water in the garden. A layer of mulch around plants acts as a barrier, reducing evaporation, controlling weeds, and regulating soil temperature.
Benefits of mulching:
- Keeps roots cool during hot weather.
- Slows down soil moisture loss.
- Reduces weed growth that competes with plants for water.
Apply mulch generously around vegetable beds, flower gardens, and trees, ensuring it doesn’t touch stems directly to prevent rot. Organic mulch breaks down over time, adding nutrients to the soil.
Capturing and Recycling Water
In addition to reducing water use, gardeners can capture and recycle water to maximize efficiency. Collecting rainwater from roofs and storing it in barrels is an excellent way to use natural precipitation. Greywater from sinks or showers (without harsh chemicals) can also irrigate gardens safely.
Tips for water recycling:
- Position rain barrels near downspouts for easy access.
- Use watering cans or hoses connected to barrels instead of direct tap water.
- Consider building a small rain garden to capture runoff and support local ecosystems.
These methods not only conserve water but also encourage a more self-sufficient, sustainable garden ecosystem.
Designing a Water-Wise Garden
Garden design can significantly influence water efficiency. Thoughtful placement of plants, paths, and irrigation lines reduces waste and makes maintenance easier.
Principles of water-wise design:
- Group plants by water requirements (hydrozoning).
- Minimize high-water-use areas like lawns.
- Use permeable surfaces to prevent runoff.
- Incorporate shade structures or trees to reduce soil evaporation.
Designing the garden with water conservation in mind ensures that each element contributes to efficiency without compromising aesthetics or functionality.
Companion Planting and Soil Cover
Certain plants provide shade or windbreaks for others, reducing water loss from evaporation. Companion planting can protect soil moisture while promoting biodiversity. Cover crops such as clover or vetch provide additional benefits by fixing nitrogen in the soil and protecting against erosion.
Ground cover plants not only reduce water evaporation but also suppress weeds, which otherwise compete for water and nutrients. These practices combine water conservation with ecological benefits.
Using Technology to Monitor Water Usage
Modern gardening technology allows for precise monitoring of water use. Soil moisture sensors, smart irrigation controllers, and weather-based irrigation apps can optimize watering schedules and detect when plants actually need water.
Smart tools for water conservation:
- Soil moisture probes provide real-time data on water levels.
- Weather-based irrigation systems adjust watering based on rainfall and humidity.
- Smartphone apps track water usage and suggest efficiency improvements.
By embracing technology, gardeners can minimize waste, save money, and ensure plants receive water only when necessary.
Community and Educational Benefits
Water-wise gardening extends beyond personal benefits; it can influence communities and promote environmental awareness. Demonstrating efficient irrigation and sustainable practices encourages neighbors and local schools to adopt similar strategies. Community gardens that implement water-saving techniques serve as educational models and inspire broader environmental stewardship.
Encouraging Wildlife and Natural Pollinators
Reducing water waste doesn’t mean sacrificing biodiversity. In fact, water-efficient gardens that incorporate native plants, mulch, and compost attract beneficial insects, pollinators, and birds. These natural allies help maintain plant health and reduce the need for chemical interventions.
By designing the garden with both water efficiency and wildlife in mind, you create a resilient ecosystem that thrives with minimal human intervention.
Gardening with a focus on water conservation is both practical and rewarding. By choosing water-efficient plants, improving soil, using smart irrigation, and designing gardens thoughtfully, it’s possible to maintain a lush, productive garden without wasting water. Simple actions like mulching, rainwater collection, and companion planting not only save water but also enhance biodiversity, reduce costs, and foster sustainable living.
Every drop saved contributes to a healthier planet and a more sustainable lifestyle. Start implementing these techniques today and watch your garden thrive while conserving water, inspiring others, and creating a greener future.

Sofia Greenfield is a sustainable gardening expert and environmental educator who inspires families and urban gardeners to cultivate green spaces responsibly. She shares practical tips on growing vegetables, herbs, and flowers using eco-friendly and recycled materials, emphasizing the joy of gardening while protecting the planet.